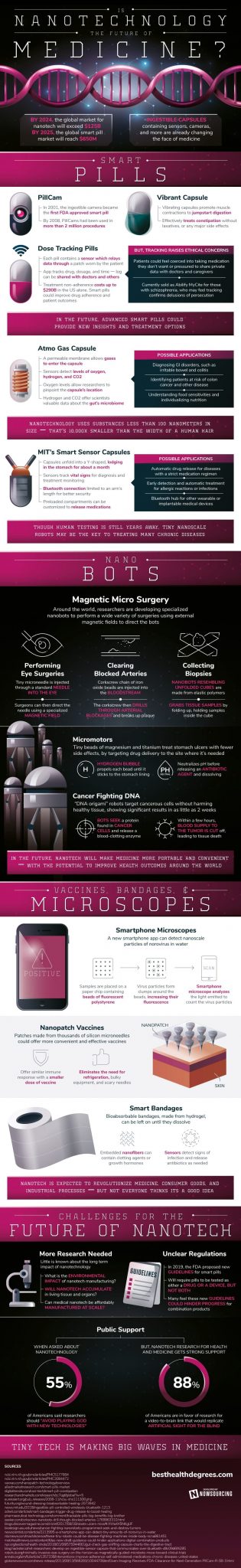
Is Nanotechnology The Future Of Medicine?
By 2024, the global market for nanotech will exceed $125B
By 2025, the global smart pill market will reach $650M
Ingestible capsules containing sensors, cameras, and more are already changing the face of medicine
Smart Pills
PillCam
In 2001, the ingestible camera became the first FDA approved smart pill
By 2008, PillCams had been used in more than 2 million procedures
Vibrant Capsule
Vibrating capsules promote muscle contractions to jumpstart digestion
Effectively treats constipation without laxatives, or any major side effects
Dose Tracking Pills
Each pill contains a sensor which relays data through a patch worn by the patient
App tracks drug, dosage, and time 一 log can be shared with doctors and others
Treatment non-adherence costs up to $290B in the US alone
Smart pills could improve drug adherence and patient outcomes
BUT, Tracking Raises Ethical Concerns
Patients could feel coerced into taking medication they don’t want or pressured to share private data with doctors and caregivers
Currently sold as Abilify MyCite for those with schizophrenia, who may feel tracking confirms delusions of persecution
In the future, advanced smart pills could provide new insights and treatment options
Atmo Gas Capsule
A permeable membrane allows gases to enter the capsule
Sensors detect levels of oxygen, hydrogen, and CO2
Oxygen levels allow researchers to pinpoint the capsule’s location
Hydrogen and CO2 offer scientists valuable data about the gut’s microbiome
Possible Applications
Diagnosing GI disorders, such as irritable bowel and colitis
Identifying patients at risk of colon cancer and other disease
Understanding food sensitivities and individualizing nutrition
MIT’s Smart Sensor Capsules
Capsules unfold into a Y-shaped, lodging in the stomach for about a month
Sensors track vital signs for diagnosis and treatment monitoring
Bluetooth connection limited to an arm’s length for better security
Preloaded compartments can be customized to release medications
Possible Applications
Automatic drug release for diseases with a strict medication regimen
Early detection and automatic treatment for allergic reactions or infections
Bluetooth hub for other wearable or implantable medical devices
Nanotechnology uses substances less than 100 nanometers in size ー That’s 10,000X smaller than the width of a human hair
Though human testing is still years away, tiny nanoscale robots may be the key to treating many chronic diseases
NanoBots
Magnetic Micro Surgery
Around the world, researchers are developing specialized nanobots to perform a wide variety of surgeries using external magnetic fields to direct the bots
Performing Eye Surgeries
Tiny microneedle is injected through a standard needle into the eye
Surgeons can then direct the needle using a specialized magnetic field
Clearing Blocked Arteries
Corkscrew chain of iron oxide beads are injected into the bloodstream
The corkscrew then drills through arterial blockages and breaks up plaque
Collecting Biopsies
Nanobots resembling unfolded cubes are made from elastic polymers
Grabs tissue samples by folding up, holding samples inside the cube
Micromotors
Tiny beads of magnesium and titanium treat stomach ulcers with fewer side effects, by targeting drug delivery to the site where it’s needed
Hydrogen bubble propels each bead until it sticks to the stomach lining
Neutralizes pH before releasing an antibiotic agent and dissolving
Cancer Fighting DNA
“DNA origami” robots target cancerous cells without harming healthy tissue, showing significant results in as little as 2 weeks
Bots seek a protein found in cancer cells and release a blood-clotting enzyme
Within a few hours, blood supply to the tumor is cut off, leading to tissue death
In the future, nanotech will make medicine more portable and convenient ー with the potential to improve health outcomes around the world
Vaccines, Bandages, & Microscopes
Smartphone Microscopes
A new smartphone app can detect nanoscale particles of norovirus in water
Samples are placed on a paper chip containing beads of fluorescent polystyrene
Virus particles form clumps around the beads, increasing their fluorescence
Smartphone microscope analyzes the light emitted to count the virus particles
Nanopatch Vaccines
Patches made from thousands of silicon microneedles could offer more convenient and effective vaccines
Offer similar immune response with a smaller dose of vaccine
Eliminates the need for refrigeration, bulky equipment, and scary needles
Smart Bandages
Bioabsorbable bandages, made from hydrogel, can be left on until they dissolve
Embedded nanofibers can contain clotting agents or growth hormones
Sensors detect signs of infection and release antibiotics as needed
Nanotech is expected to revolutionize medicine, consumer goods, and industrial processes 一 but not everyone thinks its a good idea
Challenges For The Future Of Nanotech
More Research Needed
Little is known about the long term impact of nanotechnology
What is the environmental impact of nanotech manufacturing?
Will nanotech accumulate in living tissue and organs?
Can medical nanotech be affordably manufactured at scale?
Unclear Regulations
In 2019, the FDA proposed new guidelines for smart pills
Will require pills to be tested as either a drug or a device, but not both
Many feel these new guidelines could hinder progress for combination products
Public Support
When asked about nanotechnology, 55% of Americans said researchers should “avoid playing God with new technologies”
BUT, nanotech research for health and medicine gets strong support
88% of Americans are in favor of research for a video-to-brain link that would replicate artificial sight for the blind
Tiny tech is making big waves in medicine
Sources:
https://www.mobihealthnews.com/content/fdas-new-draft-guidance-could-hinder-applications-digital-combination-products
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3084472/
https://www.zdnet.com/article/smart-bandages-trigger-drug-release-to-boost-healing/
https://www.futurity.org/wound-dressing-bioabsorbable-healing-2073942/
http://www.vaxxas.com/nanopatch-technology/overview/
https://www.newscientist.com/article/2213995-a-smartphone-app-can-detect-tiny-amounts-of-norovirus-in-water/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5177684/
https://biodesign.asu.edu/news/cancer-fighting-nanorobots-programmed-seek-and-destroy-tumors
http://blogs.discovermagazine.com/d-brief/2017/08/16/robots-ulcers-mice/#.XWa4X5NKgUF
https://www.nbcnews.com/mach/science/these-tiny-robots-could-be-disease-fighting-machines-inside-body-ncna861451
https://www.seeker.com/corkscrew-nanobots-drill-though-blocked-arteries-1769963310.html
https://robohub.org/minimally-invasive-eye-surgery-on-the-horizon-as-magnetically-guided-microbots-move-toward-clinical-trials/
https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2008-11/ncsu-shs111308.php
http://news.mit.edu/2018/ingestible-pill-controlled-wirelessly-bluetooth-1213
https://blog.hackster.io/mit-researchers-develop-an-ingestible-sensor-capsule-that-communicates-over-bluetooth-d9c09d6f4285
https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2018/01/08/575944661/gut-check-gas-sniffing-capsule-charts-the-digestive-tract
https://annals.org/aim/fullarticle/1357338/interventions-improve-adherence-self-administered-medications-chronic-diseases-united-states
https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/comment/trackable-pills-big-benefits-big-brother/
https://www.digitaltrends.com/cool-tech/smart-pill-constipation/
https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2013/08/13/566283/10044706/en/Given-Imaging-Receives-FDA-Clearance-for-Next-Generation-PillCam-R-SB-3.html
https://www.alliedmarketresearch.com/smart-pills-market
https://www.researchandmarkets.com/research/zc7qgf/global?w=5
Related: