Key Takeaways:
- You must complete a master’s level program in prosthetics that includes courses in anatomy, physiology, and prosthetic management.
- After your degree, you must get certified by the American Board for Certification in Orthotics, Prosthetics, and Pedorthics, which involves passing an exam.
- Gain hands-on experience through internships or job placements as part of your study program.
- Prosthetists work in various settings like hospitals, rehabilitation centers, and private practices.
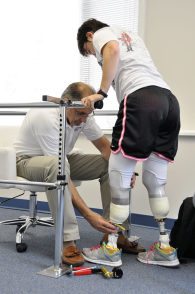
A prosthetist measures, designs, fits, and services a prosthesis. These professionals have numerous opportunities to be creative and interact with individuals whose lives have been dramatically affected by congenital deformities or amputation. If you are interested in pursuing a career in this sector, you should learn as much about the process of becoming a prosthetist as possible.
Post-Secondary Education
In general, there are four steps you will need to take in order to become a prosthetist. The first step is to gain a post-secondary education. Beginning in the year 2012, all accredited prosthetist programs were required to be at the master’s level. Entry-level master’s programs include courses in topics like anatomy, physiology, neuroanatomy, neuroscience, prosthetic management of upper and lower limbs, histology and research. Transition programs are available for students who have already attained a certificate or bachelor’s degree in the field.
Certification
The second step involved in becoming a prosthetist includes certification through the American Board For Certification (ABC). An individual who becomes ABC certified will then be a prosthetist specifically trained to manage comprehensive prosthetic patient care. The ABC states that training courses will cover patient assessments, the formulation of treatment plans, implementation of treatment plans, follow-ups, and practice management. The ABC Certified Prosthetist credentialing program is accredited through the National Commission for Certifying Agencies (NCCA). In order to attain the certification, the aspiring prosthetist must have a bachelor’s degree in prosthetics from an accredited program approved by the Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP). The other option is to have a bachelor’s degree or more in any major coupled with a prosthetics certificate from a CAAHEP accredited program.
Work Experience
Almost every post-secondary training program to become a prosthetist will include the attainment of work experience. The work term offers the prosthetist an opportunity to learn how to measure and fit prosthetic devices while also interacting with patients. All of the work is accomplished under the supervision of a medical doctor and certified prosthetist.
Obtaining A Position
A prosthetist can attain employment in medical rehabilitation facilities, hospitals, prosthetic companies, and private practices. As our medical technology continues to improve, our need for the services provided by prosthetists will increase. This is the case because doctors are capable of saving patients with injuries and illnesses that were formerly fatal, meaning that they will require prosthetic devices to ensure that they can function independently.
Although there are a plethora of steps involved in becoming a prosthetist, the process can be very rewarding. By attaining both education and experience, individuals who want to become prosthetists will attain the abstract knowledge and practical understanding to perform their jobs with excellence and expedience.
Featured articles:
- Can You Get a Degree in Nursing Online?
- How Do I Become a Dentist?
- How Do I Become a Nurse Anesthetist?
- How Do You Become a Cardiac Nurse?
- How Do You Become a Certified Nurse Midwife?
- How Do You Become a Critical Care Nurse?
- How Do You Become a Dental Hygienist?
- How Do You Become a Dermatologist?
- How Do You Become a Health Policy Nurse?
- How Do You Become a Mental Health Counselor?
- How Do You Become a Neonatal Nurse?
- How Do You Become a Nurse Educator?
- How Do You Become a Nurse Practitioner?
- How Do You Become a Pediatrician?
- How Do You Become a Pharmacist?